

The illusion of multitasking and its positive effect on performance. The role of selective attention on academic foundations: A cognitive neuroscience perspective. Sleep and attention in Alzheimer's Disease. Hennawy M, Sabovich S, Liu CS, Herrmann N, Lanctôt KL.

Sustained attention across the life span in a sample of 10,000: Dissociating ability and strategy. The Principles of Psychology, William James (1890).įortenbaugh FC, DeGutis J, Germine L, et al. First, events in other parts of the world can leave people with a sense of helplessness second, complex technology can decrease people's perceptions of control over their environment third, entrenched bureaucracies discourage people from attempting to bring about social change and fourth, the size and scope of worldwide problems contribute to people's sense of powerlessness.Classics in the History of Psychology. At least four factors can lower collective efficacy. Collective Efficacy Collective efficacy is the level of confidence that people have that their combined efforts will produce social change. Without the use of proxies, modern people would be forced to spend most of their time securing the necessities of survival. Successful living in the 21st century requires people to seek proxies to supply their food, deliver information, provide transportation, etc. Proxy Agency Bandura also recognizes the influence of proxy agency through which people exercise some partial control over everyday living. High self-efficacy and a responsive environment are the best predictors of successful outcomes. It is acquired, enhanced, or decreased by any one or combination of four sources: (1) mastery experiences or performance, (2) social modeling, or observing someone of equal ability succeed or fail at a task (3) social persuasion or listening to a trusted person's encouraging words and (4) physical and emotional states, such as anxiety or fear, which usually lowers self-efficacy.

Self-efficacy combines with environmental variables, previous behaviors, and other personal variables to predict behavior. Efficacy expectations differ from outcome expectations, which refer to people's prediction of the likely consequences of their behavior.
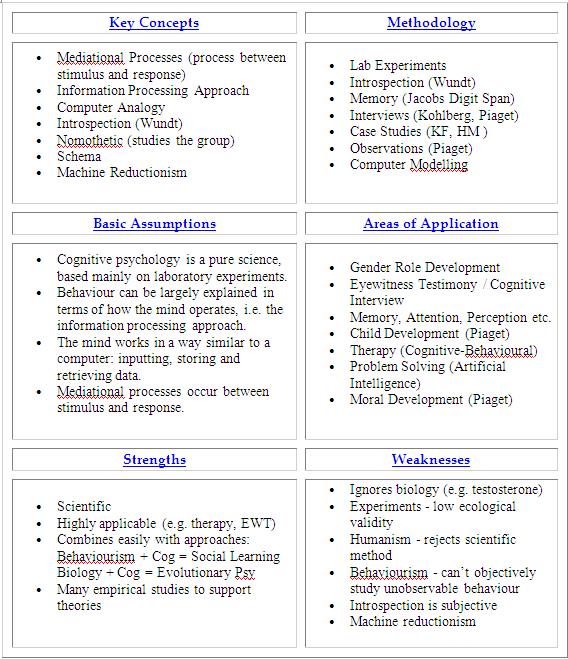
Self-Efficacy How people behave in a particular situation depends in part on their self-efficacy, that is, their beliefs that they can or cannot exercise those behaviors necessary to bring about a desired consequence. Core Features of Human Agency Human agency has four core features: (1) intentionality, or a proactive commitment to actions that may bring about desired outcomes: (2) foresight, or the ability to set goals (3) self-reactiveness, which includes monitoring their progress toward fulfilling their choices and (4) self-reflectiveness, which allows people can think about and evaluate their motives, values, and life goals. Enactive Learning All behavior is followed by some consequence, but whether that consequence reinforces the behavior depends on the person's cognitive evaluation of the situation.īandura believes that human agency is the essence of humanness that is, humans are defined by their ability to organize, regulate, and enact behaviors that they believe will produce desirable consequences. Bandura recognized four processes that govern observational learning: (1) attention, or noticing what a model does (2) representation, or symbolically representing new response patterns in memory (3) behavior production, or producing the behavior that one observes and (4) motivation that is, the observer must be motivated to perform the observed behavior. At least three principles influence modeling: (1) people are most likely to model high-status people, (2) people who lack skill or status are most likely to model, and (3) people tend to model behavior that they see as being rewarding to the model. Observational Learning The heart of observational learning is modeling, which is more than simple imitation, because it involves adding and subtracting from observed behavior. Although he believes that reinforcement aids learning, he contends that people can learn in the absence of reinforcement and even of a response. Bandura takes a broad view of learning, believing that people learn through observing others and by attending to the consequences of their own actions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
